THIRTY-sEVENTH ISSUE
june 28, 2023
High-risk Prognostic Tumor Features of Squamous Cell Carcinomas in Organ Transplant Recipients Compared With the General Population?
JAMA Dermatology
What’s worse than an uneven tan? Skin cancer!
While it is well established that solid organ transplant recipients (SOTRs) are at increased risk for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC), it is unknown whether this group is more likely to have poor cSCC outcomes compared to the general population. This dual-cohort study compared 741 cSCCs from 191 SOTRs with 2558 cSCCs from 1507 age- and sex-matched non-transplant controls. Poor prognostic cSCC features, including perineural invasion, invasion beyond the dermis, poor cellular differentiation, anatomic location, and tumor diameter >20 mm were quantified and prevalence ratios (PR) were compared.
What Did They Find?
Main Takeaways: cSCC among SOTRs is associated with significantly worse prognostic features as compared to the general population. Intensive surveillance, early diagnosis, and multidisciplinary treatment is warranted.
While it is well established that solid organ transplant recipients (SOTRs) are at increased risk for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC), it is unknown whether this group is more likely to have poor cSCC outcomes compared to the general population. This dual-cohort study compared 741 cSCCs from 191 SOTRs with 2558 cSCCs from 1507 age- and sex-matched non-transplant controls. Poor prognostic cSCC features, including perineural invasion, invasion beyond the dermis, poor cellular differentiation, anatomic location, and tumor diameter >20 mm were quantified and prevalence ratios (PR) were compared.
What Did They Find?
- Perineural invasion and invasion beyond the dermis were more than twice as common among SOTRs (PR 2.37; 95% CI 1.70-3.30 and PR 2.37; 95% CI 1.78-3.14, respectively)
- Poor cellular differentiation was more than 3x as common among SOTRs (PR 3.45; 95% CI 2.53-4.71)
- cSCC developed most frequently on the head and neck in SOTRs versus the arms and hands in the general population (285, 38.6% vs. 896, 35.2%; p<0.001)
- Tumor diameter >20 mm was moderately higher among SOTRs (PR 1.52; 95% CI 1.08-2.12)
Main Takeaways: cSCC among SOTRs is associated with significantly worse prognostic features as compared to the general population. Intensive surveillance, early diagnosis, and multidisciplinary treatment is warranted.
Lasers: Illuminating the Hidden Truth of Skin Health!
Given the increasing global prevalence of skin cancer, there is a need for faster, more precise diagnostic methods. This study describes a noninvasive skin cancer detection device, achieved by combining laser-induced plasma spectroscopy (LIPS) with deep neural network (DNN) machine learning algorithms. The primary objective of the device is to distinguish between various types of skin cancer and benign lesions.
LIPS uses ultrashort pulsed lasers to generate microplasma plumes on the surface of the skin. This enables the analysis of emitted light spectra for both elemental and molecular evaluation. Changes in the concentrations of certain elements, such as calcium, sodium, magnesium, zinc, iron, and copper within the lesions, have been linked to the development and progression of cancer. Using a single-channel spectrometer, emission signals from the skin surface are captured and processed through the DNN model, and a "diagnosis" is provided based on the results.
What did they find:
Main takeaway: While further research is warranted, the combination of LIPS and DNN in a noninvasive device show promise in its ability to distinguish between cancerous and benign skin lesions with a high level of sensitivity and specificity.
Given the increasing global prevalence of skin cancer, there is a need for faster, more precise diagnostic methods. This study describes a noninvasive skin cancer detection device, achieved by combining laser-induced plasma spectroscopy (LIPS) with deep neural network (DNN) machine learning algorithms. The primary objective of the device is to distinguish between various types of skin cancer and benign lesions.
LIPS uses ultrashort pulsed lasers to generate microplasma plumes on the surface of the skin. This enables the analysis of emitted light spectra for both elemental and molecular evaluation. Changes in the concentrations of certain elements, such as calcium, sodium, magnesium, zinc, iron, and copper within the lesions, have been linked to the development and progression of cancer. Using a single-channel spectrometer, emission signals from the skin surface are captured and processed through the DNN model, and a "diagnosis" is provided based on the results.
What did they find:
- The sensitivity for diagnosing non-melanocytic skin cancer ranges from 56-90%
- The accuracy of diagnosis for malignant melanoma ranges from 49-81%
- The sensitivity and specificity for differentiating skin cancers from benign lesions using LIPS and the DNN-based algorithm were 94.6% (95% CI: 92.0%-97.2%) and 88.9% (95% Cl: 85.5%-92.4%), respectively
Main takeaway: While further research is warranted, the combination of LIPS and DNN in a noninvasive device show promise in its ability to distinguish between cancerous and benign skin lesions with a high level of sensitivity and specificity.
What are the rates of positive surgical margins after treatment of vulvar melanoma and are positive margins associated with survival?
Dermatologic Surgery Journal
Vulvar melanoma: a vulgar melanoma with a vengeance!
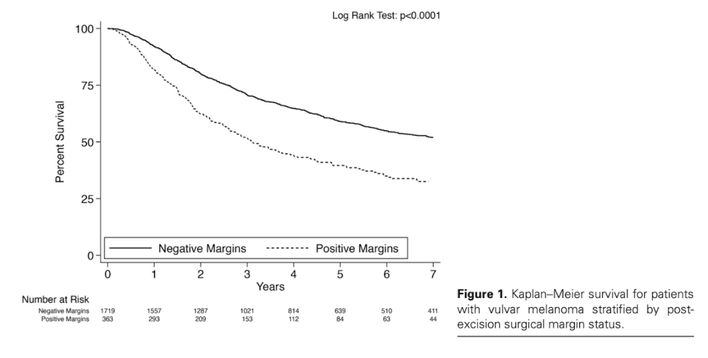
Vulvar melanoma is both rare and dangerous, with a 27-47% 5-year survival rate and high chance of recurrence. To date, there are no consensus guidelines on treatment of vulvar melanoma. While current guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network exist, they are based on data gathered from truncal and extremity melanomas, rather than vulvar or any specialty site melanomas. This is likely due to the lack of data on vulvar melanoma treatments and outcomes. In this 15-year retrospective cohort study, 2,226 excised vulvar melanomas were analyzed from the National Cancer Database. The survival outcomes and rates of positive margins after standard excision, stratified by tumor stage, were examined.
What did they find?
Vulvar melanoma is both rare and dangerous, with a 27-47% 5-year survival rate and high chance of recurrence. To date, there are no consensus guidelines on treatment of vulvar melanoma. While current guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network exist, they are based on data gathered from truncal and extremity melanomas, rather than vulvar or any specialty site melanomas. This is likely due to the lack of data on vulvar melanoma treatments and outcomes. In this 15-year retrospective cohort study, 2,226 excised vulvar melanomas were analyzed from the National Cancer Database. The survival outcomes and rates of positive margins after standard excision, stratified by tumor stage, were examined.
What did they find?
- 17.2% (SE: 0.8%) of lesions had positive margins post-excision
- T4 tumors had the highest rate of positive margins at 22.9% (SE: 1.5%)
- Different treatments (partial, total, and radical vulvectomy) showed similar rates of positive margins
- Positive surgical margins were associated with an increased 42% hazard of death (HR 1.42, p < 0.001; 95% CI 1.217-1.657
Limitations: Analysis of survival was not disease specific and both local recurrence data and exact margins taken during standard excision were unavailable.
Main Takeaways: There is a high rate of positive margins after standard excision of vulvar melanoma. Updated guidelines for vulvar melanoma may be needed.
Main Takeaways: There is a high rate of positive margins after standard excision of vulvar melanoma. Updated guidelines for vulvar melanoma may be needed.
Do leave-on cosmetic antimicrobial preservatives affect the healthy skin resident Staphylococcus epidermidis?
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology
Not all bugs are bad!
Leave-on cosmetic products are filled with antimicrobial preservatives to maintain safety, quality, and extend shelf-life. The role of preservatives on the skin microbiome is unclear; thus, researchers set out to evaluate the antimicrobial effect of nine cosmetic preservatives on Staph epidermidis, a resident of the skin microbiome that has been shown to protect against inflammation, infections, and cancer.
77 S. epidermidis isolates were taken from healthy skin samples. Isolates were diluted and inoculated on MH agar with minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of 9 leave-on cosmetic preservatives: benzyl alcohol, 2-bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol, ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), imidazolidinyl urea, 2-phenoxyethanol, sodium benzoate, sodium salicylate, and trans, trans-2,4-hexadienoic acid potassium salt.
What did they find:
Main takeaway: At maximum permitted doses, certain preservatives can completely clear S. epidermidis isolates and thus the inhibitory effects of preservatives in cosmetic products should be re-evaluated to maintain the healthy balance of the skin microbiome.
Leave-on cosmetic products are filled with antimicrobial preservatives to maintain safety, quality, and extend shelf-life. The role of preservatives on the skin microbiome is unclear; thus, researchers set out to evaluate the antimicrobial effect of nine cosmetic preservatives on Staph epidermidis, a resident of the skin microbiome that has been shown to protect against inflammation, infections, and cancer.
77 S. epidermidis isolates were taken from healthy skin samples. Isolates were diluted and inoculated on MH agar with minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of 9 leave-on cosmetic preservatives: benzyl alcohol, 2-bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol, ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), imidazolidinyl urea, 2-phenoxyethanol, sodium benzoate, sodium salicylate, and trans, trans-2,4-hexadienoic acid potassium salt.
What did they find:
- Each preservative showed the same MIC to all S. epidermidis isolates, except CTAB
- Benzyl alcohol, CTAB, ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, and 2-phenoxyethanol at the MIC dose killed 107 CFU/mL of S. epidermidis in 3 hours
- CTAB and ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate at maximum dose (1 mL and 4.8 mL respectively) completely cleared S. epidermidis in less than 1 hour
- 2-bromo-2-nitro-1,3-propanediol, and imidazolidinyl urea at maximum doses (1 mL and 6 mL respectively) showed complete clearance of S. epidermidis in 8 hours
Main takeaway: At maximum permitted doses, certain preservatives can completely clear S. epidermidis isolates and thus the inhibitory effects of preservatives in cosmetic products should be re-evaluated to maintain the healthy balance of the skin microbiome.
MMP9, friend or foe?
Etanercept, a TNF-⍺ inhibitor, effectively abrogates epidermal detachment in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (SJS/TEN), but the mechanism is poorly understood. TNF-⍺ upregulates the expression of epidermal matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), a collagenase involved in the degradation of type IV basement membrane collagen, leading researchers to investigate its role in SJS/TEN.
Researchers compared MMP9 expression in SJS/TEN (n=17), nonbullous adverse drug reaction (n=28), and normal control (n=11) skin samples using rtPCR. Healthy skin explants were exposed to serum from SJS/TEN patients for 72 hours and treated with etanercept. MMP9 expression was compared using immunohistochemistry.
What did they find?
Main takeaways: TNF-⍺-induced MMP9 expression is the proposed mode of action for etanercept treatment and pathogenesis of SJS/TEN, identifying MMP9 as a potential therapeutic target.
Etanercept, a TNF-⍺ inhibitor, effectively abrogates epidermal detachment in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (SJS/TEN), but the mechanism is poorly understood. TNF-⍺ upregulates the expression of epidermal matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), a collagenase involved in the degradation of type IV basement membrane collagen, leading researchers to investigate its role in SJS/TEN.
Researchers compared MMP9 expression in SJS/TEN (n=17), nonbullous adverse drug reaction (n=28), and normal control (n=11) skin samples using rtPCR. Healthy skin explants were exposed to serum from SJS/TEN patients for 72 hours and treated with etanercept. MMP9 expression was compared using immunohistochemistry.
What did they find?
- MMP9 expression in the epidermal basal layer was significantly higher in SJS/TEN skin samples when compared to nonbullous adverse drug reaction skin (P=0.0054) and healthy control skin (P=0.015)
- Healthy skin explants exposed to SJS/TEN patient serum showed a significant increase in epidermal MMP9 expression compared to controls
- Treatment with etancerpt showed a significant reduction in MMP9 expression in the epidermal basal layer of healthy skin explants exposed to SJS/TEN patient serum
Main takeaways: TNF-⍺-induced MMP9 expression is the proposed mode of action for etanercept treatment and pathogenesis of SJS/TEN, identifying MMP9 as a potential therapeutic target.